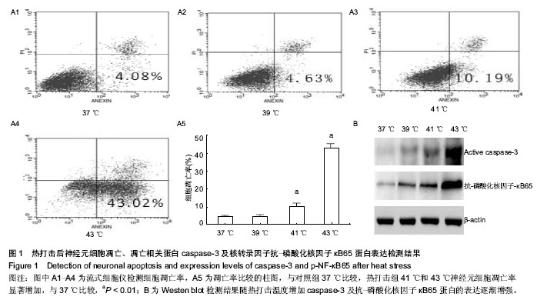
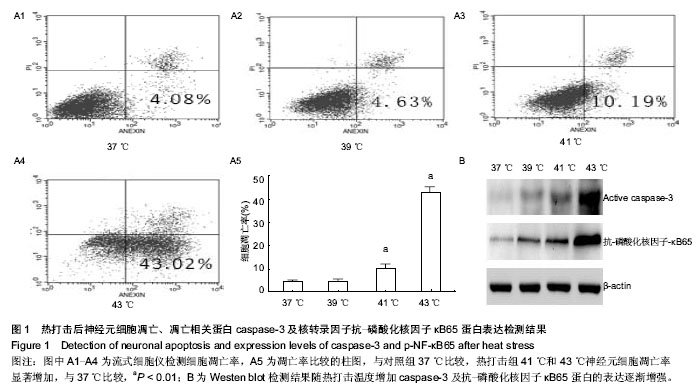
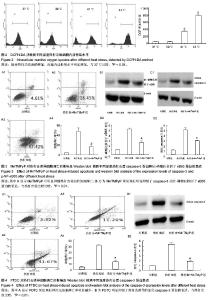
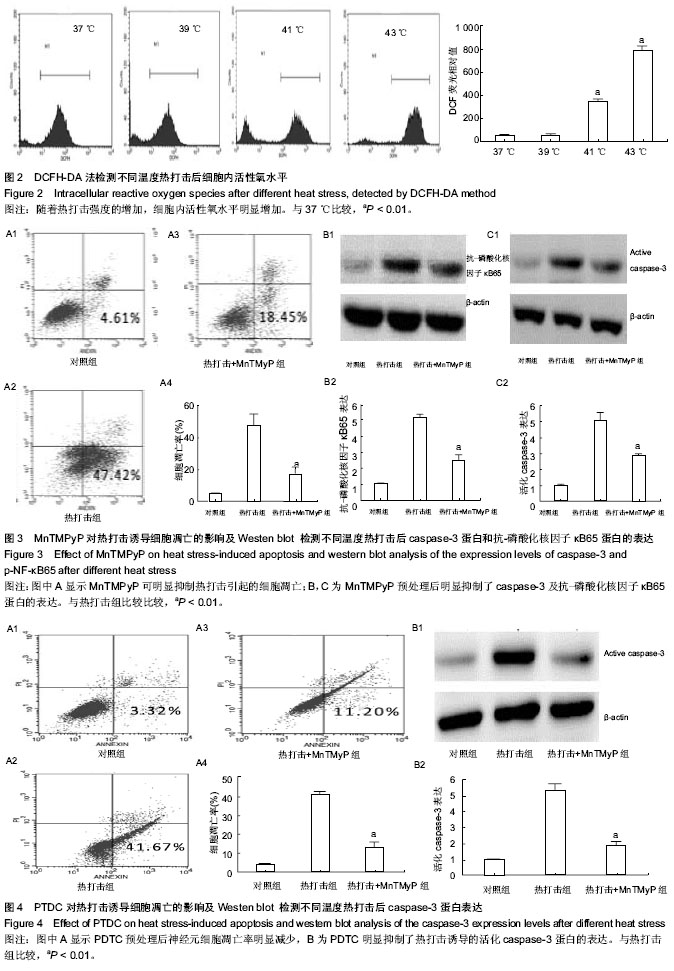
| [1] Casa DJ, Armstrong LE, Kenny GP, et al.Exertional Heat Stroke: New Concepts Regarding Cause and Care.Sideline and Eventmanagement.2012;11(3):115-123.[2] Bouchama A,Knochel JP.Heat stroke.N Engt J Med. 2002;346: 1978-1988.[3] 刘志锋,苏磊.胃肠功能障碍与炎症反应在中暑发病机制中的作用[J].广东医学杂志,2010,31(6):787-788.[4] Leon LR, Helwig BG. Heat stroke: Role of the systemic inflammatory response.J Appl Physiol.2010;109:1980-1988.[5] 刘志锋,唐柚青,苏磊,等.热打击后小鼠肺和脑组织病理学的改变[J].中华急诊医学杂志, 2011,20(6):623-626.[6] ChingWei L,ChinLin P,YiShin H, et al.Multiple Organ Failure Caused by Non-exertional Heat Stroke After Bathing in a Hot Spring.J Chin Med Assoc.2010;73(14):212-215.[7] Roberts GT, Ghebeh H, Chishti MA,et al.Microvascular Injury, Thrombosis, Inflammation, andApoptosis in the Pathogenesis of Heatstroke A Study in Baboon Model. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.2008;28:1130-1136.[8] Pallepati P, Averill-Bates DA. Mild thermotolerance induced at 40 ℃protects HeLa cells against activation of death receptor-mediated apoptosis by hydrogen peroxide.Free Radical Bio Med.2011;50:667-679.[9] Li Y.Induction of DNA fragmentation after 10 to 120 minutes of focal cerebral ischemia in rats.Stroke.1995;26:1252.[10] 张水文.热射病时中枢神经系统变化研究进展[J].解放军预防医学杂志,2000,18(4):307-309.[11] Vogel P, Dux E, Wiessner C. Evidence of apoptosis in primary neuronal cultures after heat shock.Brain Res.1997;764(1-2): 205-213.[12] Chang CK,Chang CP,Liu SY, et al. Oxidative stress and ischemic injuries in heat stroke.Progress Brain Res.2007; 162: 525-545.[13] Liu Y,Li CP,Zhu L. Oxidative stress,lipid peroxidation and liver cell apoptosis play a important role in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Med Recap.2008;14(10):1468-1470.[14] 魏燕,辛晓燕.活性氧调控的细胞凋亡信号[J].现代肿瘤医学杂志, 2011,19(2)371-373.[15] Mustafi SB, Chakraborty PK, Dey RS,et al. Heat stress upregulates chaperone heat shockprotein 70 and antioxidant manganese superoxide dismutase through reactive oxygen species (ROS),p38MA PK,and Akt.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2009;14(6):579-589.[16] Tan GY, Yang L, Fu YQ,et al. Effects of different acute high ambient temperatures on function of hepatic mitochondrial respiration, antioxidative enzymes, and oxidative injury in broiler chickens.Poultry Science.2010;89(1):115-122.[17] Iida R, Ueki M, Yasuda T. A Novel Transcriptional Repressor, Rhit, Is Involved in Heat-Inducible and Age-Dependent Expression of Mpv17-Like Protein, a Participant in Reactive Oxygen Species Metabolism. 2010;30(10):2306-2315.[18] Wright CJ, Agboke F, Muthu M,et al. Nuclear Factor-κB (NF-κB) Inhibitory Protein IκBβ Determines Apoptotic Cell Death following Exposure to Oxidative Stress.JBC. 2012; 287(41): 6230-6239.[19] Kim GW,Copin JC,Kawase M,et al. Excitotoxicity is required for induction of oxidative stress and apoptosis in mouse striatum by the mitochondrial toxin,3-nitropropionic acid. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.2000;20(1):119-129.[20] Luetjens CM,Bui NT,Sengpiel B. Delayed mitochondrial dysfunction in excitotoxic neuron death:cytochrome c release and a secondary increase in superoxide production. J Neurosci. 2000;20 (15):5715-5723.[21] 祁伯祥,林小娟,杨于嘉.NF-κB和神经细胞凋亡[J]. 国外医学:生理病理科学与临床分册,2003,23(2):122-124.[22] Yang CY, Lin MT. Oxidative Stress in Rats With Heatstroke-Induced Cerebral Ischemia.Stroke. 2002;33(3): 790-794.[23] 刘晓敏,肖军军,董晓敏,等. 应用细胞培养、流式细胞技术和Western Blot 检测氮杂糖化合物SZL在体外抑制人宫颈癌HeLa细胞增殖与诱导凋亡的效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(42):8536-8540.[24] Hinz M,Krappmann D,Eichten A,et al.NF-kappa B function in growth control :regulation of cyclin D1 expression and G0PG12 to2S2phase transition. Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19(4): 2690-2698.[25] Sharp F R,Lu A ,Tang Y,et al.Multiple molecular penumbras after focal cerebral ischemia.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.2000; 20:1011-1018.[26] Speir E. Cytomegalovirujs gene regulation by reactive oxygen species. Agents in atherosclerosis.1Ann NY Acad Sci. 2000; 5899:363-374.[27] Lawrence T.The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.2009;1:a1651.[28] Nizamutdinova IT, Guleria RS, Singh AB,et al.Retinoic acid protects cardiomyocytes from high glucose-induced apoptosis through inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2013;228(2):380-392.[29] Schneider A,Martin WA,WeihH,et al.NF-kappa B is activated and promotes cell death in focal cerebral ischemia.Nat Med. 1999;5(5):554-559.[30] Qin Z,Wang Y,Chasea TN.A caspase-3 like protease is involved in NF-kappaB activation induced by stimulation of N-methyl-D as par ate recepors in rats triatum. Brain Res Mol Brain.2000;80(2):111-122.[31] Domanska JK, Bronisz KA , Zajac H, et al.Inter-relations between nuclear-factor kappaB activation,glial response and neuronal apoptosis in gerbil hippo campus after ischemia. Acta Neuro biol Exp(Warsz).2001;61:45-51.[32] 张勤丽, 牛侨.细胞凋亡机制概述[J].环境与职业医学. 2007, 24(1): 102v-107v.[33] Maizo I,Susin SA,Petit PX,et al.Caspases disrupt mitochondrial membrane barrier function.FEBS Lett.1998; 427(2):198-202.[34] Camandola S,Mattson MP.Pro-apoptotic action of PAR-4 in voives inhibition of NF-κB activity and suppression of Bcl-2 expression. J Neurosci Res.2000;61(2):134-139.[35] Iida R, Ueki M, Yasuda T. A Novel Transcriptional Repressor, Rhit, Is Involved in Heat-Inducible and Age-Dependent Expression of Mpv17-Like Protein, a Participant in Reactive Oxygen Species. Metabolism.2010;30(10):2306-2315.[36] Tan GY, Yang L, Fu YQ,et al. Effects of different acute high ambient temperatures on function of hepatic mitochondrial respiration, antioxidative enzymes, and oxidative injury in broiler chickens. Poultry Science.2010;89(1):115-122 |